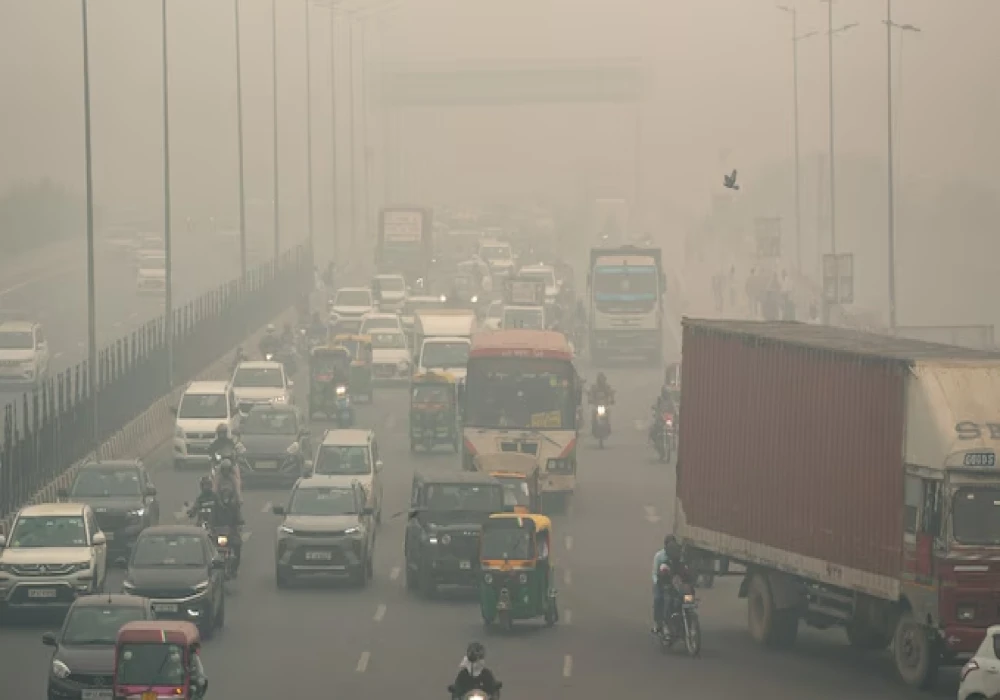
Delhi is facing a serious air pollution crisis, with the air quality index (AQI) staying in the "severe plus" category for several days. AQI levels above 450 indicate extremely unhealthy air, which can harm people's health, especially those with existing health issues.
To address this emergency, Delhi's Environment Minister, Gopal Rai, has called for the Central government and Prime Minister Narendra Modi to step in. One suggestion is to use cloud seeding to create artificial rain, which could temporarily improve the air quality.
What Is Cloud Seeding?
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique designed to create rain artificially. It involves adding chemicals like silver iodide, dry ice, or potassium iodide to clouds. These substances act as "seeds," helping water droplets form around them and eventually causing rainfall.
The process can be done using planes, rockets, or machines on the ground. Once the chemicals are released into the clouds, they work to increase precipitation, which could help reduce dust and pollutants in the air.
Why Consider Cloud Seeding in Delhi?
Delhi’s air pollution is caused by many factors, including vehicle emissions, industrial pollution, construction dust, and smoke from crop burning in nearby states. During winter, the situation worsens as cold weather traps pollutants closer to the ground.
Rain could temporarily improve air quality by washing away harmful particles in the air. By using cloud seeding, the government hopes to bring some relief to the people of Delhi, who are struggling with breathing difficulties and other health problems.
How Much Will It Cost?
A proposal for cloud seeding has been made by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur. According to their estimates, cloud seeding could cost about ₹1 lakh per square kilometer. This project would require both funding and coordination between multiple agencies to implement successfully.
Is Cloud Seeding Effective?
The effectiveness of cloud seeding is still being debated. While it has been shown to increase rainfall in certain cases, its impact on reducing air pollution is not well understood.
Experts point out that cloud seeding works only when there are suitable clouds with enough moisture. If Delhi’s weather conditions do not meet these requirements, the process may not work.
Concerns About Cloud Seeding
While cloud seeding may seem like a quick fix, it comes with challenges and risks:
- Chemical Impact: Introducing chemicals like silver iodide into the atmosphere could have unknown environmental effects in the long term.
- Temporary Relief: Even if it works, cloud seeding would only provide short-term relief. Pollution levels could rise again once the rain stops.
- Focus on Long-Term Solutions: Many experts believe that the government should focus on addressing the root causes of air pollution, such as reducing emissions from vehicles, factories, and construction.
Challenges in Implementation
Conducting cloud seeding in Delhi is not easy. It requires:
- Suitable weather conditions with moist clouds.
- Advanced equipment, like airplanes and ground-based machines.
- Coordination between scientists, government agencies, and weather departments.
If these conditions are not met, the project could fail to deliver results.
What Experts Say
While cloud seeding might help temporarily, scientists warn against relying on it as a long-term solution. They stress the need for stricter pollution control measures, such as:
- Encouraging public transport to reduce vehicle emissions.
- Enforcing rules to limit industrial pollution.
- Banning the burning of crop stubble in nearby states.